Pigs and Hearts: Science, Medicine, and Meaning

The phrase “pigs and hearts” may sound unusual, but it carries deep meaning in science, medicine, and culture. Pigs have long played a vital role in human society—not just as livestock, but as key contributors to medical research and organ transplantation.
In recent years, groundbreaking experiments have shown that pig hearts can be transplanted into humans, offering hope to thousands waiting for heart transplants. At the same time, pigs and hearts carry symbolic weight in culture, literature, and religion.
This article will explore the fascinating connections between pigs and hearts, covering:
- Medical breakthroughs in pig-to-human heart transplantation.
- Why pigs are suitable for heart research.
- Cultural symbolism of pigs and hearts.
- Ethical considerations of using animals in medicine.
- Future possibilities for this field.
Why Pigs Are Linked to Hearts in Medicine
Anatomical Similarities
Pigs are often used in medical research because their organs closely resemble human organs in size and function. Pig hearts, in particular, are:
- Similar in structure and physiology to human hearts.
- Large enough to support blood circulation in humans.
- Easier to study and modify genetically.
Medical Uses of Pigs
- Xenotransplantation – Transferring pig organs into humans.
- Heart Valves – Pig heart valves have been used in human surgeries for decades.
- Research Models – Pigs are used to study heart disease and treatments.
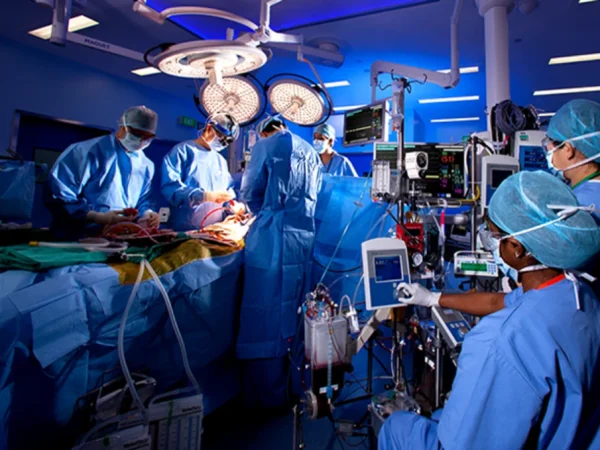
Pig Heart Transplants: A Medical Breakthrough
One of the biggest milestones in “pigs and hearts” is the development of pig-to-human heart transplants.
The First Transplants
- In 2022, doctors performed the first genetically modified pig heart transplant into a human patient.
- The patient survived for two months, proving the procedure was possible.
Why Pig Hearts?
- Thousands of patients die each year waiting for heart transplants.
- Pig hearts could provide an unlimited supply of donor organs.
- Genetic modification reduces the risk of rejection.
Challenges Ahead
- Preventing immune system rejection.
- Avoiding animal viruses transferring to humans.
- Long-term studies on survival and quality of life.
Pig Heart Valves in Human Surgery
Even before whole heart transplants, pig hearts have been saving lives for decades through bioprosthetic valves.
- Pig (porcine) valves are harvested, treated, and implanted in humans.
- Commonly used to replace diseased or damaged heart valves.
- Preferred for older patients because they don’t require lifelong blood thinners.
This widespread use shows that the connection between pigs and hearts is already part of mainstream medicine.
Cultural Symbolism of Pigs and Hearts
Beyond science, pigs and hearts both carry rich symbolic meaning.
Pigs in Culture
- In many traditions, pigs symbolize abundance, fertility, and nourishment.
- In some religions, pigs are considered unclean animals.
- Pigs appear in literature (e.g., Animal Farm) as metaphors for human behavior.
Hearts in Culture
- Universally associated with love, emotion, and life.
- The heart symbol is one of the most recognized icons worldwide.
- In spiritual traditions, the heart is often seen as the seat of the soul.
Pigs + Hearts Together
- Sometimes used symbolically in art to represent the intersection of science and humanity.
- “Pig heart” as a phrase has been used in music and literature to explore raw emotion and survival.
Ethical Issues with Pig Heart Transplants
The use of animals in medicine raises serious ethical questions.
Animal Welfare Concerns
- Pigs used for transplants are often genetically modified and raised in controlled environments.
- Animal rights activists argue that using pigs in this way is unethical.
Religious Concerns
- Some faiths (Judaism, Islam) prohibit contact with pigs.
- Raises questions about whether pig-derived organs are acceptable for patients of these religions.
Medical Ethics
- Should humans rely on animal organs instead of focusing on artificial or lab-grown alternatives?
- Is the potential to save lives enough to justify the practice?
Alternatives to Pig Hearts
While pig hearts are promising, scientists are also exploring other solutions.
- Artificial Hearts
Mechanical devices that pump blood.
Useful as temporary solutions but not yet a full replacement.
- Lab-Grown Organs
Using stem cells to grow human-compatible hearts.
Still in early stages of development.
- 3D Bioprinting
Printing human tissues and organs layer by layer.
Could reduce reliance on animals in the future.
Benefits of Pig-to-Human Heart Research
- Could solve the organ shortage crisis.
- Save thousands of lives annually.
- Provide insights into human heart disease.
- Create opportunities for other organ transplants (kidneys, lungs, livers).
Challenges Facing Pig Heart Transplants
Despite progress, many hurdles remain:
- Immune System Rejection – Even with genetic modification, human bodies may attack pig organs.
- Infection Risk – Concerns about viruses from pigs entering human populations.
- Ethical Resistance – Pushback from religious groups and activists.
- Cost and Accessibility – High-tech transplants may be expensive at first.
Future of Pigs and Hearts in Medicine
Experts believe pig heart transplants may become a regular medical practice in the next 10–20 years.
What’s Coming:
- Safer genetic modifications to prevent rejection.
- Larger-scale clinical trials.
- Acceptance in mainstream healthcare.
- Alternatives like lab-grown hearts working alongside pig organs.
The future of pigs and hearts is full of promise, but careful regulation and ethical discussion will be needed.
Conclusion
The connection between pigs and hearts is more than symbolic—it represents one of the most exciting frontiers in modern medicine. From pig heart valves already saving lives to experimental pig-to-human heart transplants, pigs are central to solving the global organ shortage.
At the same time, pigs and hearts carry cultural, religious, and ethical weight that shapes how we view this scientific progress. The challenge is finding a balance between saving lives and respecting ethical boundaries.
As technology advances, pigs may play an even bigger role in the future of human health—keeping not just hearts, but hope, alive.
FAQs
1. Why are pig hearts used in medicine?
Because they are similar in size and structure to human hearts, making them good candidates for transplants and research.
2. Are pig heart valves safe for humans?
Yes. Pig valves have been used for decades and are a proven medical solution.
3. Can someone live with a pig heart?
Yes, but long-term success is still being studied. Early cases have shown survival for weeks to months.
4. Are pig heart transplants ethical?
Opinions differ. Some see it as a life-saving breakthrough, while others object on animal welfare or religious grounds.
5. Will pig hearts replace human donors?
They may help fill the shortage, but lab-grown and artificial hearts are also being developed.
Also read: Prime Dent: 10 Incredible Benefits of Choosing Expert Dental Care